Difference between biotic and abiotic factors
to understand the difference between biotic and abiotic, we need to understand first how they are made up.
Our world is full of various things, some of them are common to us and others amaze us because of their rarity; Likewise, there are living beings, elements, or objects that lack life. In biology, ecology, and other natural sciences, biotic beings are considered promoters of life and the study of abiotic factors as functional inorganic elements for scientific evolution.
An ecosystem is a system made up of a group or a community of living beings plus the place or physical environment in which they inhabit (biotope). Within this unity, living beings are all interdependent. In one way or another, they are all part of a chain in which the slightest imbalance or imbalance can have great consequences. All the units that make up an ecosystem can be divided into biotic factors or abiotic factors.
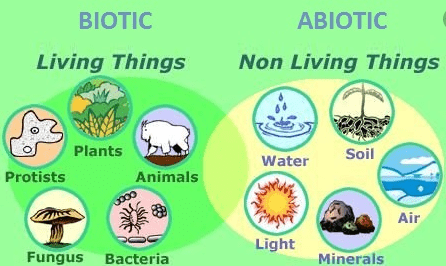
As their names indicate, the former refers to living beings and the latter to those that do not have life. Both biotic and abiotic factors play a very important role in shaping an ecosystem.
Within an ecosystem, a series of factors that interact to maintain balance in that ecosystem and globally, that is, between ecosystems, are combined. Among these, we differentiate biotic factors such as those organisms that are alive, from abiotic factors or non-living elements of the ecosystem.
To understand what biotic and abiotic factors are in reference to the characteristics and particularities that define these elements, it is necessary to bear in mind their interrelation and dependence with a higher structure in which these factors are integrated, the ecosystem.
In this Green Ecology article, we explain the difference between biotic and abiotic, their definitions, and how they interact with each other.
Speaking of things that have or do not have life, below we explain what is the difference between biotic and abiotic; so that you know what each concept refers to.
The ecosystem, therefore, and from the perspective of biotic and abiotic factors, could be defined as the interaction between living organisms (Biocenosis) and non-living elements (Biotope) of a specific part of the environment where their relationships result in a coherent unit of organization of the same.
Ecology identifies the study of living beings with biotic factors, while abiotic or physical factors will focus on the study of non-living components of the environment surrounding the species, allowing their development and survival.
A quantifying the availability of essential resources such as light solar, water, oxygen, inorganic matter, or minerals present in the ecosystem, we can determine which organisms can survive and which natural elements prevail in a particular place.
Biotic factors | Abiotic factors |
Definition | |
| Biotic factors are all living organisms that are part of an ecosystem. | Instead, abiotic factors are those that do not have life. Abiotic factors, like biotic factors, are considered elements of an ecosystem. |
Role | |
| Biotic factors influence the way an ecosystem develops. Although many may think that they outweigh abiotic factors, the truth is that both are equally important. Flora and fauna do not actively determine and cannot change factors such as temperature or the amount of water available. However, they can affect each other and in this way, help determine the conformation of an ecosystem. | These play very important roles within the lives of biotic factors, since ultimately they are the determinants, for example, of the type of flora and fauna that inhabit a given place. Biotic factors must adapt to abiotic factors in order to survive. For example, the animals and plants that inhabit a desert have evolved and adapted to survive the characteristic conditions of this ecosystem. |
Examples | |
| Regarding biotic factors, flora and fauna, together with their interactions, are the only two representatives of these. | On the other hand, some of the best examples of abiotic factors include water, sunlight, soil, moisture levels, pH, nutrients, and oxygen. |
Key differences between abiotic factors and biotic factors
Biotic factors are all the beings that are or were alive in the ecosystem. They develop in the biosphere and are capable of reproducing.
Some examples of biotic factors are animals, plants, fungi, and other similar organisms. It does not matter if they have an autotrophic or heterotrophic diet, if the organism has life then it belongs to biotic factors.
Biotic factors are characterized by directly or indirectly interfering with the life of other living organisms, as well as the environment. They affect individuals, the population, the community, and the biosphere.
Biotic
The word biotic refers to living beings, taking into account that the fauna as well as the flora are units that, given their evolutionary characteristics such as their birth, development, and death, make them belong to biotic elements.
Biotic beings determine the existence of others of the same species to keep track of other living structures.
Definition of biotic with examples and factors
The biotic factors of an ecosystem are all those beings that are part of it and that have life. To be considered living organisms they must be made up of at least one cell and fulfill vital functions, like any living organism: nutrition (including respiration), interaction (including all relationship processes), and reproduction. In this way, any biotic factor has the ability to feed, interact with its environment, and have offspring that ensure the continuity of the species.
Thus, we classify biotic factors into producing, consuming, and decomposing organisms. Then, we divide them into the five biological kingdoms :
- The Animalia kingdom is made up of all animals.
- The kingdom Plantae is formed by all plant organisms.
- The Fungi kingdom is made up of fungi.
- The Monera kingdom is made up of microorganisms such as bacteria or viruses.
- The Protista kingdom is formed by those eukaryotic cells, but which are not classified within the fungi, Animalia, or Plantae kingdoms.
What are the biotic factors?
We can easily establish the definition of biotic factors as all those that have life, that is, all those included in any of the kingdoms of life defined by biology.

The interaction between the biotic factors included in an ecosystem (normally we will refer to the flora and fauna of a given environment) will consequently lead to their survival and reproduction.
The biotic factors are arranged generally in populations, ie sets of living beings of the same type that share a specific habitat. Another way to organize will refer to the so-called trophic (food) chains between species, through the competition between living beings for food and the interdependent relationships between them at the same time.
They are distinguished from abiotic factors in that they are not related to life as such, but to the surrounding matter and its chemical, climatic, physical processes, etc. non-organic type.
How We Classify Biotic Factors
Biotic factors are classified according to the role or capacity of action that they develop in their respective ecosystems:
Producer or autotrophic organisms
They produce their own food. Living beings synthesize their forms of energy from non-organic matter, for example, plants, do from sunlight and water (photosynthesis).
Read Also: Difference Between Photosynthesis and Respiration
Consuming or heterotrophic organisms
They feed on other living things. Living things that consume organic matter are obtained from other living things to support their metabolism. These living beings can be of two types:
Herbivores
Those that feed on plants, seeds, roots, algae, or vegetables.
Predators
Those who hunt and devour the meat of other consumers.
Decomposing of organisms
Living things that feed on decomposing organic matter, forming part of the essential process of “recycling” and “recirculation” of matter and energy.
Examples of biotic factors
- Forests and Forest Masses serve as habitats for many species and supply constant organic matter to detritophages in the soil.
- Fungi and Insects, the main decomposing organisms, reduce decomposing organic matter (dead leaves, pieces of bark, remains of dead animals, shedding of skin, excrement) assimilating the nutrients they need and leaving the rest to incorporate them back into the balanced energy of the ecosystem.
- Large predators such as cats, snakes, and birds of prey that feed on smaller animals, keep their populations under control and regularly favor the incorporation of more organic matter with their death to recycle and reintroduce the energy flow.
- Marine phytoplankton is composed of a variety of photosynthetic microorganisms that support the entire marine trophic pyramid and is the food for larger forms such as crustaceans and cetaceans.
- Large herbivores such as cattle, antelopes, wildebeests, elephants, etc . feed on tons of organic plant matter, subsequently serving as sustenance for the great predators and scavengers that will come later.
Abiotic
They are chemical or physical factors that affect the ecosystem, but unlike biotics, they do not have life. Examples of abiotic elements are water, light, moisture, minerals, and gases.
Something very interesting about this is that abiotic factors can affect the abilities that living things have to survive. In the same way, they affect the environment and communities.
In contrast to living or tangible beings, the word abiotic groups together elements that within their nature do not contain the cycles of life. That is, these are not part of living beings. Such is the case of water, earth, wind, and fire.
They are physical components existing within reality but that do not integrate evolutionary characteristics designated by nature.
What are the abiotic factors?
In contrast to the previous definition, abiotic factors will be those elements of a physical or chemical nature that intervene in the characterization of a given ecosystem. The abiotic factors present in the environment are also called inert factors, such as geological or geographical.

They can be connected to environmental factors, such as climate or soil dynamics. The term abiotic is usually used in ecology to indicate everything that is part or product of organic life as it is identified on our planet.
Another peculiarity of abiotic factors is that they have direct effects on biotics, influencing their evolution (through adaptation processes, for example, or natural selection) and in turn, biotic factors can transform the nature of the former.
An example of what has been described above is the salinity level of sea waters, which can affect resident species, allowing those capable of adapting to proliferate and those that do not become extinct or migrate to other regions. Similarly, the proliferation of certain types of microorganisms can increase or decrease the concentration of certain substances in water, modifying their chemical constitution.
Definition of abiotic with examples and factors
They are those factors that are not living beings, do not have a life of their own, or are inert. They do not perform the vital functions of any living organism, however, they are very important, since they form the physical space in which biotic factors or living organisms live, that is, biotic factors could not exist without these inert or lifeless factors.
These factors can be divided into natural and artificial factors. The natural ones are those that are part of our planet in a natural way such as air, light, soil, water, or rocks and artificial factors are those that are the product of human activity such as marble or a bottle made of plastic. In addition, some biotic factors can become abiotic factors, such as the example of a living organism that dies and becomes matter that enriches the soil.
Other abiotic factors more complex than the previous ones are climate, temperature, humidity, pH, or the presence of different seasons, and are more complex since they depend on the interaction of multiple other factors. These factors also influence the ecosystem and the beings that live in it.
Abiotic and biotic factors are influencing factors
Abiotic factors influence all living factors in an ecosystem, being able to become limiting factors for the growth of a species, thus limiting (directly or indirectly) its survival and reproduction. Therefore, they are determining factors in terms of the type and number of organisms capable of inhabiting that particular ecosystem. Abiotic factors influence the body itself, other living things, their relationships, and the waste they generate.
A simple example of the interaction between biotic and abiotic factors is that of plants with factors such as water, sunlight, or available carbon dioxide. Plants use water to survive and sunlight and carbon dioxide to create their own food through photosynthesis.
Another example, some ecosystems suffer winters with very low temperatures and a lot of snow. Some animals, such as the Arctic fox, adapt to these abiotic factors thanks to the development of a thick layer of white fur during colder times.
Biotic factors are also influencing factors. For example, decomposing organisms such as bacteria or fungi decompose the remains of inert organisms. This is a mechanism that manages to return the components of these organisms to the earth, which in turn later returns to living beings, thus closing the cycle.
In summary, all the ecosystems of the planet are made up of both biotic and abiotic factors and these are not static factors, but rather interact with each other to give rise to the conditions of that ecosystem. For example, in the image below we can see abiotic factors such as seawater, beach sand, and the air itself, which are what allow biotic factors such as palm trees and seagulls in the image to live in an environment suitable for them.
How do we classify abiotic factors
Abiotic factors can be classified according to their nature:
Physical abiotic factors
They are those related to the forces that act on ecosystems on Earth, for example:
- Sunlight, the planet’s main source of energy and affects the temperature of large masses of water, air, and land, which heat up and expand during the day and cool and contract at night.
- The temperature influences the possible development of life and the type of relations of a biotope.
- The atmospheric pressure, exerted on the different elements of an ecosystem, is also a determining factor.
- The climate, with great relevance in the processes that occur within the different ecosystems.
- The relief affects both temperature and atmospheric pressure (the higher the altitude, the lower the pressure and the lower the temperature).
Chemical abiotic factors
They are those related to the constitution of matter and the different reactions that occur with this matter in different ecosystems, for example:
- pH, the chemical property of the media (water or soil) indicating its level of acidity or alkalinity. A very acidic or very alkaline medium is corrosive and contrary to organic life.
- Soil chemistry, the amount and type of chemical elements present in the soil are decisive when defining its characteristics.
- Air chemistry, the development of life, and most biological processes have to do with the exchange of gases for animal respiration and photosynthesis. The characteristics of the air facilitate or impede the development of ecosystems, being able to subject them to demanding conditions.
- Water chemistry, characteristics such as salinity, the concentration of nutrients or dissolved oxygen level, as well as the presence of pollutants, etc. determine the quality of the water to support life and therefore the type of ecosystem that can develop.
Biotic and Abiotic Factors: A Necessary and Inseparable Relationship
Although they do not harbor life in themselves, abiotic factors are fundamental for the development and survival of biotic factors. Without abiotic factors, biotic factors could not exist and any alteration of the former would also affect the latter.
Among the main problems that affect these factors are the processes of pollution and environmental degradation and of course climate change, significantly increased by human action.
Conclusion: Differences between biotic and abiotic
- The word biotic designates life and everything related to nature in conjunction with its organic cycles.
- The abiotic is related to biocenosis that integrates climatic characteristics, and terrestrial, and aquatic physical spaces.
- Biotic factors originate from living beings and their products that condition or give life to other compounds.
- Abiotic factors appear due to the influence of the physical and chemical components of the environment (water, soil, wind, fire).
- Biotic elements are producers of other beings, which gives way to the stability and evolution of nature.
- Abiotic elements are inorganic, and their functionality is related to the fusion of their same components referred to as scientific evolution, such as wind together with gases.