Difference between Ions and Free Radicals
Ions and free radicals are both types of atoms or molecules that have an electric charge. However, there are several key differences between ions and free radicals.
Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, giving them a net positive or negative charge. They are stable and do not readily react with other substances. Free radicals, on the other hand, are atoms or molecules that have an unpaired electron in their outer shell, giving them a net positive or negative charge. They are highly reactive and can readily react with other substances, often leading to the formation of new free radicals in a process known as chain reactions.
One of the main differences between ions and free radicals is their stability. Ions are generally stable and do not readily react with other substances, while free radicals are highly reactive and readily react with other substances.
Another difference is that ions are usually formed as a result of an atom or molecule gaining or losing electrons in a chemical reaction, while free radicals are often formed through the breaking of chemical bonds or by exposure to radiation or other forms of stress.
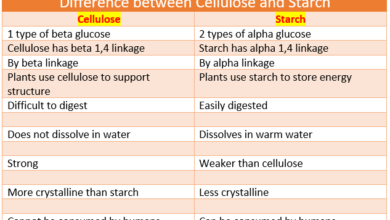
Difference between ions and free radicals in Tabular Form
| Property | Ions | Free Radicals |
|---|---|---|
| Charge | Positive or Negative | Positive or Negative |
| Stability | Stable | Unstable |
| Formation | Gain or lose electrons | Break chemical bonds or exposure to radiation or stress |
| Reactivity | Low | High |
| Occurrence in nature | Common | Uncommon |
| Role in chemical reactions | Passive | Active |
| Role in biological processes | Passive | Active |
| Role in environmental processes | Passive | Active |
| Toxicity | Low | High |
| Role in human health | Both positive and negative | Both positive and negative |
| Detection | Easy | Difficult |
| Impact on materials | Minimal | Significant |
| Impact on energy levels | Minimal | Significant |
| Impact on chemical equilibrium | Minimal | Significant |
What is Ion?
An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, giving it a net positive or negative charge. The term “ion” comes from the Greek word “ion,” which means “to go.” This refers to the fact that ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons and are therefore capable of moving through a solution or a material.
Ions can be either positive or negative, depending on whether they have gained or lost electrons. Atoms that have gained electrons are called anions, and they have a negative charge. Atoms that have lost electrons are called cations, and they have a positive charge. Molecules that have gained or lost electrons can also become ions, and they are called molecular ions.
Ions are formed through a process called ionization, which occurs when atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons. Ionization can be caused by various factors, including exposure to radiation, chemical reactions, or the application of heat or pressure.
Examples of ions include sodium ions (Na+), chloride ions (Cl-), calcium ions (Ca2+), and oxygen ions (O2-). These ions are commonly found in chemical compounds and play important roles in various chemical and biological processes. For example, sodium ions are important for maintaining the proper balance of electrolytes in the body, and chloride ions are important for regulating the acidity of a solution.
There are two major forms of ions:
Anions: These are ions that have a negative charge, usually due to the fact that they have gained one or more electrons. Examples of anions include chloride (Cl-), bromide (Br-), and sulfate (SO42-).
Cations: These are ions that have a positive charge, usually due to the fact that they have lost one or more electrons. Examples of cations include sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), and magnesium (Mg2+).
What is Free Radical?
A free radical is an atom or molecule that has an unpaired electron in its outer shell, giving it a net positive or negative charge. The term “free radical” comes from the Latin word “radix,” which means “root.” This refers to the fact that free radicals are atoms or molecules that are highly reactive and can readily react with other substances, often leading to the formation of new free radicals in a process known as chain reactions.
Free radicals are highly reactive and can readily react with other substances, often leading to the formation of new free radicals. They are often formed through the breaking of chemical bonds or by exposure to radiation or other forms of stress. Free radicals can be either positive or negative, depending on their charge. Positively charged free radicals are called cations, while negatively charged free radicals are called anions.
Examples of free radicals include the hydroxyl radical (OH·), the superoxide radical (O2·-), and the nitrogen dioxide radical (NO2·). These free radicals are commonly found in the environment and play important roles in various chemical and biological processes. However, they can also be harmful to live organisms, as they can cause damage to cells and tissues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ions and free radicals are both atoms or molecules that have an electric charge. However, there are several key differences between the two, including their stability, reactivity, and role in chemical reactions. Ions are stable and do not readily react with other substances, while free radicals are highly reactive and readily react with other substances, often leading to the formation of new free radicals.