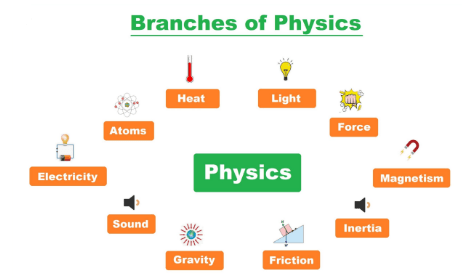
Branches of Physics
the term “physics” comes from the Greek word “Physica” which means nature. so, it is a science that deals with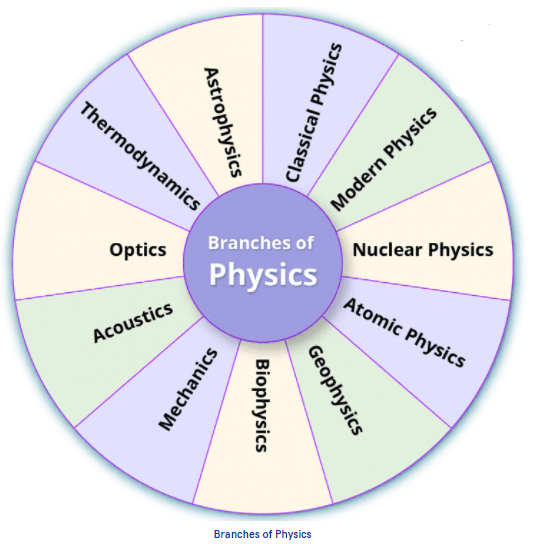 the relationship between space, time, matter, and energy. classical physics, modern physics, and Contemporary physics are three major branches of physics. however, it is further subdivided into numerous branches and fields.
the relationship between space, time, matter, and energy. classical physics, modern physics, and Contemporary physics are three major branches of physics. however, it is further subdivided into numerous branches and fields.
along with other branches of science such as biology, chemistry, etc, physics revolutionized human life around us.
“Science is the knowledge of logical reasoning.”
so, A man has always wanted to observe, think and reason about the world around him. the man tried to find ways to organize the disorder in the observed facts about the natural phenomena and material things in an orderly manner which results in a single discipline of science, called natural Philosophy.
Classification of the Study of Nature
the study of nature may be classified into two branches:
- Biological Science: the science of living things is known as biological science.
- Physical Science: the science of non-living things is known as natural science.
What is Physics?
Physics is the branch of science concerned with the properties of matter and energy and the relationship between them. it also deals with the motion and behavior of particles and objects. in other words, physics is basically the study of how objects behave. it is an important and basic part of physical science. it is an experimental science.
List of Branches of Physics
- Classical Physics
- Modern Physics
- Mechanics
- Geophysics
- Biophysics
- Acoustics
- Heat & Thermodynamics
- Electromagnetism
- Optics
- Sound
- Hydrodynamics
- General Relativity
- Quantum Mechanics
- Quantum Computer
- Atomic Physics
- Astrophysics
- Molecular Physics
- Nuclear Physics
- Solid-State Physics
- Particle Physics
- Super Conductivity
Basic Pillars of Physics
there are four fundamental pillars and areas of interest in physics on a theoretical basis. these pillars enable us to reach the different phenomena of matter. these are not the branches of physics but only structures in the different fields of physics. the four pillars are as follows:
- Classical Mechanics
- Thermodynamics
- Classical electrodynamics
- Quantum mechanics
What are the main frontiers of fundamental science?
there are three main frontiers of fundamental science.
- the world of extremely large 1.e. universe
- the world of extremely small (i.e. particles such as electrons, protons, neutrons, mesons, and others.
- the world of middle-sized things (from molecules at one extreme to the earth at the other). it is a world of complex matter.
Some new Branches of Physics and Their Role in developing the technology
Branches of Physics: by the end of the 19th century many physicists started believing that everything about physics has been discovered. however, at the beginning of the 20th century, many new experimental facts revealed that the laws formulated by the previous investigators need modification.
- Nuclear Physics: the branch of physics that deals with atomic nuclei are called nuclear physics.
- Particle Physics: the branch of physics which is concerned with the ultimate particles of which matter is composed is called particle physics.
- Relativistic mechanics: the branch of physics with deals with velocities approaching that of light is called relativistic mechanics.
- Solid-State Physics: the branch of physics which is concerned with the structure and properties of solids is called solid-state physics.
Other Branches of Physics
Physics is the most fundamental of all sciences and provides other branches of science, basic principle, and fundamental laws. this overlapping of physical and other fields gives birth to new branches.
Astrophysics
the branch of physics concerned with the chemical and physical properties, origin, and evolution of the celestial bodies. it also involves applying the laws of physics and chemistry for explaining the birth, life, and death of stars. the planets, galaxies, nebulae, and other bodies like that are also discussed in astrophysics. this branch of science also has siblings with cosmology.

Atomic physics
the branch of physics that studies the atoms that make up matter and the interactions that exist between them. it deals with the following topics: the structure of the atom, Photons, the Photoelectric Effect, Black body Radiation, etc.
Biophysics
the branch of physics deals with the scientific study of the biological process in terms of the laws of physics. for example, echolocation in bats, stresses, and strains in skeletal muscular structures.
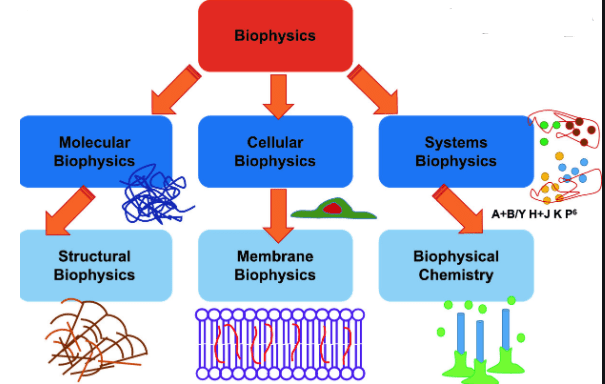
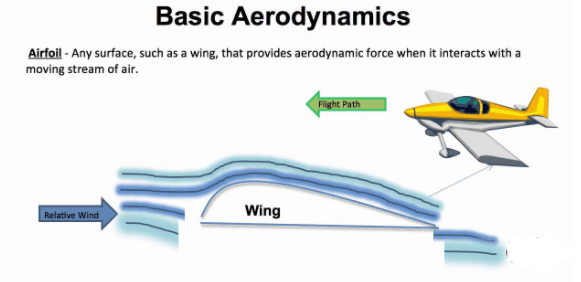
Aerodynamics
the branch of physics which deals with the study of the movement of air and other gases. it includes the study of the interactions of air with moving objects, such as airplanes, and of the effects of moving air on stationary objects such as buildings.
Cosmology
the branch of physics which deals with the behavior of the material universe in its entirety. it is one of the widest subjects in the spectrum of physics.
Physical Chemistry
the branch of chemistry that is concerned with the physical structure of the chemical compound, the amount of energy they have, the way they react with other compounds, and the bonds that hold their atoms together.
Physical Oceanography
it is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the oceans. especially the motion and physical properties of the ocean’s water.
Medical Physics
it is the application of physics to medicine. it generally concerns physics as applied to medical and radiotherapy.
Geophysics
it is the physics of the earth and its environment in space. its subjects include the shape of the earth, its gravitational and magnetic field, dynamics of the earth as a whole and component parts, the earth’s internal structure composition and tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation, the hydrological cycle including snow and ice, all aspects of the oceans, the atmosphere, ionosphere, magnetosphere, and solar-terrestrial relations, and analogous problems associated with the moon and other planets.
Engineering Physics:
it is an academic degree, available mainly at the levels of B. Tech, B.Sc, M.Sc, and P.Hd, unlike other engineering degrees( such as aerospace engineering or electrical engineering), EP does not necessarily include a particular branch of science or physics.
instead, EP provides a more thorough grounding in applied physics of any area chosen by the student ( such as optics, nanotechnology, microfabrication, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, control theory, aerodynamics, energy, or solid-state physics).
Plasma
plasma is a gas in which an important fraction of the atoms is ionized so that the electrons and the ions are separately free. in physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized.
the basic premise is that heating a gas dissociates its molecular bonds, rendering it into its constituent atoms. further heating leads to ionization (a loss of electrons), turning it into plasma containing charged particles, positive ions, and negative electrons.
the presence of a non-negligible number of charge carriers makes the plasma electrically conductive so that it responds strongly to electromagnetic fields. plasma, therefore, has properties quite unlike those of solids, liquids, or gases and is considered a distinct state of matter.
like gas, plasma does not have a definite shape or a definite volume unless enclosed in a container; unlike gas, under the influence of a magnetic field, it may form structures such as filaments, beams, and double layers. some common plasma in stars and neon.
Photonics
the branch of physics that studies photons and is considered a part of quantum mechanics. the photons are elementary particles that are associated with electromagnetic fields.
Magnetohydrodynamics
Magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics is the branch of physics that studies the dynamics of electrically conducting fluids. examples of such fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and saltwater. the word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from the magneto-meaning magnetic field, hydro-meaning liquid, and dynamics-meaning movement.
the idea of MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which create forces on the fluid, and also change the magnetic field itself. it is also known as space plasma physics.
it is the study of plasmas as they occur naturally in the universe. it is a fundamental part of the study of space weather and has important implications not only for understanding the universe but also for practical everyday life. including the operation of communications and weather satellites. it is unique from other fields as astrophysics which study a similar phenomenon, in that space physics utilizes measurements from high-altitude rockets and spacecraft.
Superfluidity
it is a state of matter in which the matter behaves like a fluid without viscosity and with infinite thermal conductivity. the substance which looks like a liquid will flow uncontrollably, and also will be at exactly the same temperature throughout itself. superfluidity is the frictionless flow and other exotic behavior of electrons in a superconducting solid.
Superconductivity
it is an electrical resistance of exactly zero which occurs in certain materials below a characteristic temperature. superconductivity is a phenomenon observed in several metals and ceramic materials. when these materials are cooled to temperatures ranging from near absolute zero (o degrees Calvin, -273 Celcius) to liquid nitrogen temperatures (77k, -196c), their electrical resistance drops with a jump down to zero.
the temperature at which electrical resistance is zero is called the critical temperature (Tc) and varies with the individual material. for practical purposes, critical temperatures are achieved by cooling materials with either liquid helium or liquid nitrogen.
because these materials have electrical resistance, meaning electrons can travel through them freely, they can carry large amounts of electrical current for long periods of time without losing energy as heat. superconducting loops of wire have been shown to carry electrical currents for several years with no measurable loss.
this property has implications for electrical power transmission, if transmission lines can be made of superconducting ceramics, and for electrical storage devices.
Optics
it is the branch of physics that involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light.
Hydrodynamics
the branch of physics which deals with the dynamics of fluids, especially incompressible fluids, in motion. it is concerned with the mechanical properties of fluids. it tells how quickly an object can travel in a fluid. example: a person swimming in water.
Electromagnetism
it is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature the other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.
electromagnetism is the force that causes the interaction between electrically charged particles; the areas in which this happens are called electromagnetic fields. electromagnetism is responsible for practically all the phenomena encountered in daily life, with the exception of gravity.
ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. electromagnetism is also the force that holds electrons and protons together inside atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. this governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons inside and between atoms.
Role of Physics in Technology
- Physics also plays an important role in the development of technology and engineering.
- science and technology are vital forces for change in the outlook of mankind.
- the information media and the fast means of communication have brought all parts of the world in close contact with one another.
- events in one part of the world immediately reverberate around the globe.
- we are living in the age of information technology.
- computer networks are products of chips developed from the basic ideas of physics. the chips are made of silicon. silicon can be obtained from the sand.
- it is up to us whether we make a sandcastle or a computer out of it.
Careers in Physics
Physics Branch | Career Importance |
| Classical & Modern Physics | Classical & Modern Physics Degree Holder can be:
|
| Atomic physics | the specialist in follower degree Might be a:
|
| Nuclear Physics | the following Degree Holder can be a:
|
| Astrophysics | An Astrophysicist might be a:
|
| Thermodynamics | He will be a Good:
|
| Optics | An Optic Degree Holder might be a:
|
| Acoustics | he should apply for the following Posts:
|
| Mechanics | he can be a Rheologist. |
| Biophysics | Being a biophysicist and academic teacher is a good job for him. |
| Geophysics | He will be a Geophysicist. |
Branches of Physics video illustration
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Mention the 7 Branches of Physics.
The 7 branches are Thermodynamics which studies Temperature and Heat. Mechanics deals with Motion and it causes interactions between objects. Optics That studies the Light includes mirrors, lenses, and colors as well. The next one is Electromagnetism, the theory of Relativity, and Quantum Mechanics.
What are the Three Main Branches of Physics?
Here are the 8 major branches of Physics:
- Classical Physics
- Modern Physics
- Nuclear Physics
- Atomic Physics
- Geophysics
- Biophysics
- Mechanics
- Acoustics
What are The two Divisions of Physics?
Physics is the branch of science that deals with matter and energy, it also studies the motion of objects. classical physics and modern physics are two main divisions and pillars of physics.
Who is the father of Physics?
Galileo Galilei is known as the father of modern physics who introduced the experimental scientific method and also he was the first scientist who used refracting telescopes for the research of many important astronomical discoveries. so, He also laid the foundation of astronomy.
You May Also Like: